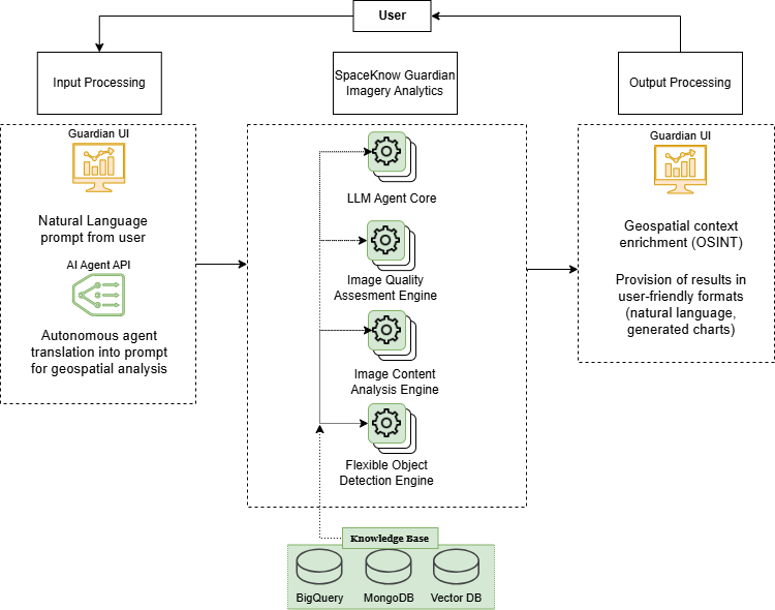
Objectives of the Product
Maritime routing and compliance reporting commonly rely on fragmented inputs: marine weather products of uneven skill, separate onboard logs and regulatory formats that demand manual reconciliation. Limited traceability drives conservative routing, frequent captain overrides of optimisation advice, higher fuel and GHG emissions and disputes where ‘what conditions actually occurred’ is difficult to evidence.
SOAR addresses this trust and performance gap through an end-to-end platform that connects data, decisions and evidence. It continuously ingests Earth observation data, AIS tracks and onboard telemetry, then time-aligns them, runs quality checks, and records provenance (where the data came from and how it was processed).
A fusion layer blends these sources to produce consistent marine weather fields and confidence metadata. On top, AI models improve short-term forecasts and translate sensor signals into sea-state conditions (e.g., GNN-GRU with physics-aware bias correction), providing frequent updates.
In parallel, SOAR estimates GHG emissions and generates compliance outputs aligned with EU ETS, EU MRV, and IMO DCS. Key datasets and reports are anchored in a tamper-evident permissioned ledger to support audits and dispute resolution. Targets include ≥20% better short-term accuracy than existing providers <10s dashboard responses, and ±5% emissions accuracy.
Customers and their Needs
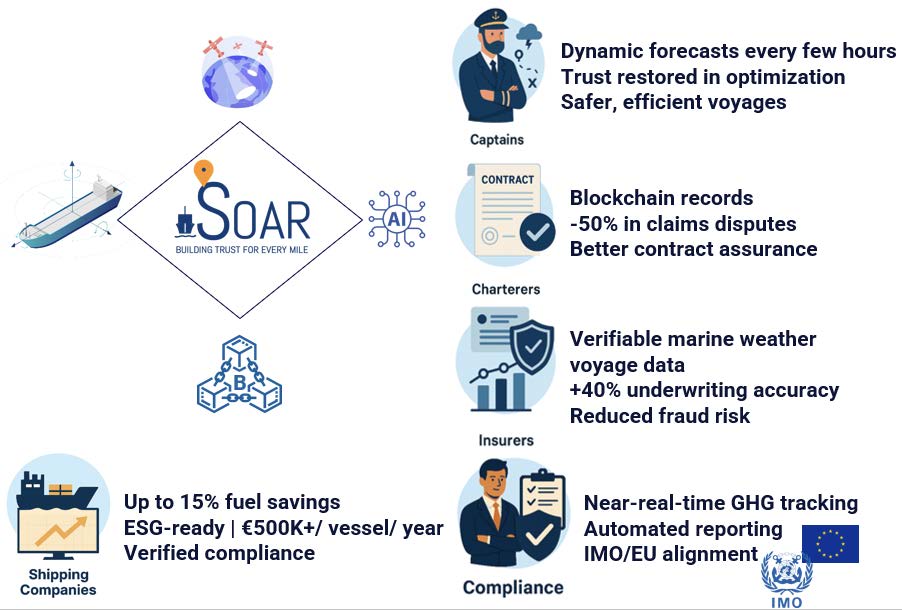
SOAR targets shipping companies and fleet operators as primary customers, with captains’ teams, fleet performance managers and compliance/ESG officers as core end-users. Secondary customers and users include chartering teams, cargo owners/charterers, insurers and reinsurers, ports/offshore stakeholders, and voyage-optimisation or compliance software providers that integrate marine weather data and emissions intelligence via APIs.
Maritime operators need routing guidance they trust in practice: frequent, accurate forecasts that reflect observed conditions, clear confidence indicators, and evidence that supports decisions. They also need automated emissions monitoring and outputs aligned with EU ETS, EU MRV and IMO DCS to reduce manual reporting burden, errors and audit risk.
Charterers and insurers need independently defensible voyage reconstructions (conditions, routes, emissions) to accelerate claims handling, charter-party performance assessments and dispute resolution.
Integrators need stable, well-documented interfaces and provenance-rich data products to embed SOAR into existing workflows. Across all groups, needs include secure access control, GDPR-aligned handling of operational data, and tamper-evident records suitable for audits. These stakeholders are involved through requirements validation with early supporters and pilot partners/planning, vessel integration activities, and iterative feedback on dashboards, reports and API payloads to ensure operational fit.
Targeted customer/users countries
Primary focus: EU shipping operators and stakeholders exposed to EU ETS/EU MRV obligations (including operators trading to/from EU ports), with initial engagement anchored in Greece through the consortium and pilot ecosystem.
Secondary reach: international maritime operators, charterers, and insurers involved in EU and global trades and audit/compliance workflows.
Product description
SOAR is a cloud-native, microservice-based marine weather intelligence platform that integrates onboard telemetry, AIS and multi-source EO/reanalysis/forecast datasets into a unified data layer. A streaming ingestion service performs time-alignment, QA/QC, normalisation and provenance tagging; a fusion engine generates marine weather analyses (winds, waves, currents). The AI forecast suite combines data assimilation and spatiotemporal models (e.g., GNN-GRU) with physics-aware bias correction (PINN + wavelet residuals) to deliver rolling 0–72h forecasts plus 4–10-day outlooks, exposed through dashboards and APIs.
A routing component consumes the latest analyses and constraints to produce route recommendations and scenario comparisons; benefit targets include improved route adherence and fuel savings ranges used in the business case (e.g., 5–15%). An emissions module segments voyages, applies vessel-specific emission factors, propagates uncertainty, and formats outputs aligned with EU ETS, EU MRV and IMO DCS. A permissioned integrity layer anchors hashes of key datasets/reports to create tamper-evident, auditable voyage records.
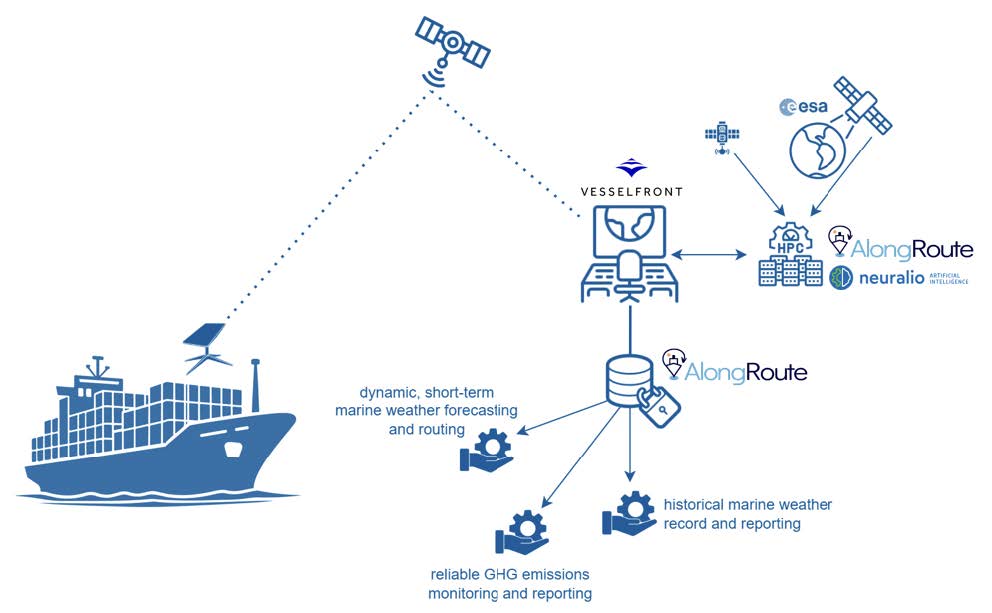
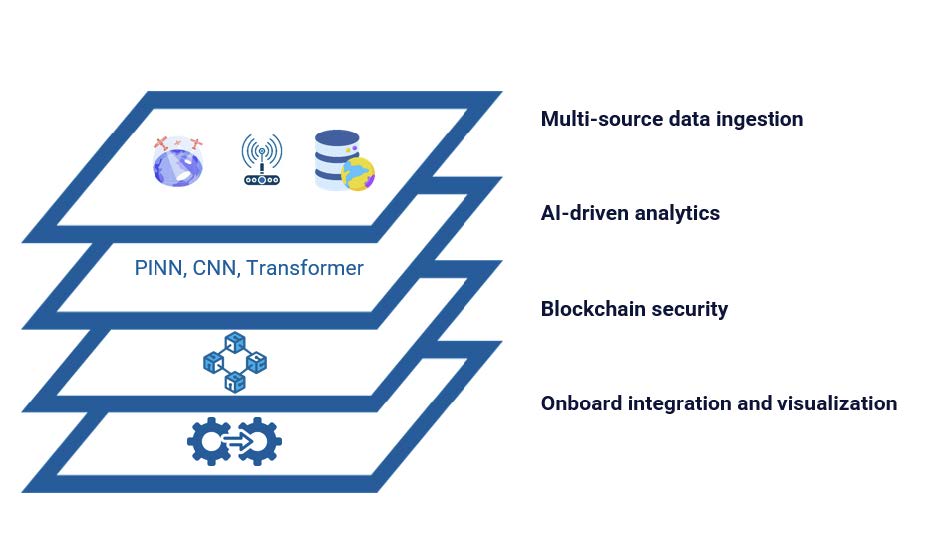
Added Value
SOAR brings added value by addressing the adoption barrier that limits many marine weather services: maritime operators do not trust recommendations built mainly on numerical models or third-party forecasts, with limited linkage to what the vessel actually experienced. This drives overrides, inconsistent fuel consumption, and weak audit readiness. Many market alternatives sit in one slice of the value chain, marine weather intelligence, route optimisation, EO data services, or measurement hardware, leaving operators to stitch together data, reconcile assumptions, and defend outputs during disputes.
SOAR stands out because it links what was observed, what was decided and what was reported in one traceable chain. It combines Earth observation and reanalysis data with AIS and onboard telemetry to build a view of sea-state conditions along the route, and it reconstructs each voyage so users can clearly connect marine weather forecasting to routing decisions and resulting emissions.
Its AI models use onboard measurements to refine local sea-state conditions and reduce systematic marine weather forecast errors, which increases confidence and helps maritime operators make safer and smarter decisions. Finally, SOAR anchors key datasets and reports in a permissioned, tamper-evident record, providing evidence that is useful for charter-party claims, insurance underwriting, and EU ETS/EU MRV/IMO DCS audits. Everything is delivered through one platform (dashboards and APIs), reducing the need to stitch together multiple vendors.
Current Status
SOAR is in the product development and integration phase. The end-to-end architecture is defined, covering streaming ingestion, multi-source fusion, AI forecasting, emissions accounting, integrity anchoring, and the dashboard/API layer.
Initial versions of the ingestion and QA/QC pipelines and the fusion workflow operate in a development/test environment, enabling time-aligned processing of onboard telemetry, AIS and EO/reanalysis inputs. Early AI forecasting components have been exercised on historical datasets to benchmark reconstruction/forecast skill against reference baselines. A permissioned ledger environment for tamper-evident logging is configured for test deployments, alongside cloud-native microservices for scalable processing.
Work in progress includes expanding the data catalogue (public and commercial EO and partner feeds), refining model performance and uncertainty handling, integrating emissions algorithms and report formats (EU ETS, EU MRV, IMO DCS), and iterating dashboards and API payloads with early adopters and pilot stakeholders to confirm operational workflow fit